It’s the longest sequence of tasks that needed to be done in order for a project to be completed. They are called critical because if they are to be delayed, the entire project will be delayed. Finding the critical path is crucial since it allow managers to be able to estimate the project duration and identify task dependencies. As well as to be able to create realistic schedules.
We use the CPM algorithm to define the amount of time needed to complete the tasks at hand. There are common critical paths calculated using Gantt Charts nowadays, which make the whole procedure easier.
What is the Critical Path Method(CPM)?
The CPM approach, sometimes referred to as critical path analysis (CPA), involves constructing a network diagram to illustrate the order in which tasks must be carried out in order to complete a project. The duration of these tasks sequences is determined once they have been created in order to locate the crucial path.
Why is (CPM) Important in Project Management
Projects are the summation of small important tasks that needed to be scheduled. This maybe seem easy, but without mapping it, your project scope can easily drift away and you would find that the project is suddenly out of hands. We talked about Project Scope earlier, feel free to check it out here: WHAT IS A PROJECT MANAGEMENT SCOPE?
Using the Critical Path method is important when dealing with the project since it marks all tasks the crucial tasks. Critical path analysis can help you with the following:
Recognize resource limitations, task dependencies, and project dangers.
Calculate each task’s duration with accuracy
Project scheduling and resource allocation are aided by prioritizing tasks based on their float or idle time.
Determine which jobs are essential and make sure they are finished on time.
Track the status of your project and gauge timetable deviation
Utilize schedule compression strategies like rapid tracking or crash duration
Critical Path Examples
The following is an example of CPM diagram Provided be Projectmanager.com that can help you visualize what does it mean.
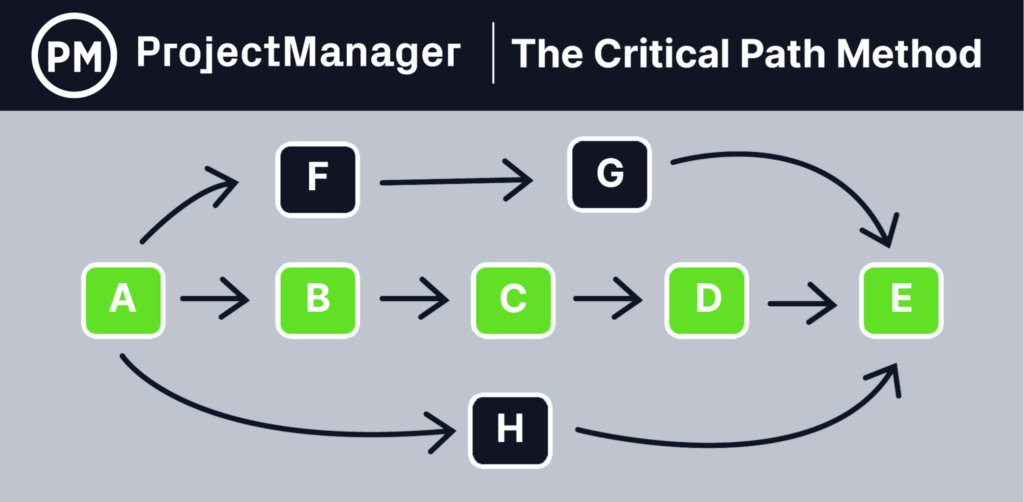
As shown above, letters represent tasks and critical paths are marked by the green letters. As well as demonstrating that F and B are parallel tasks.
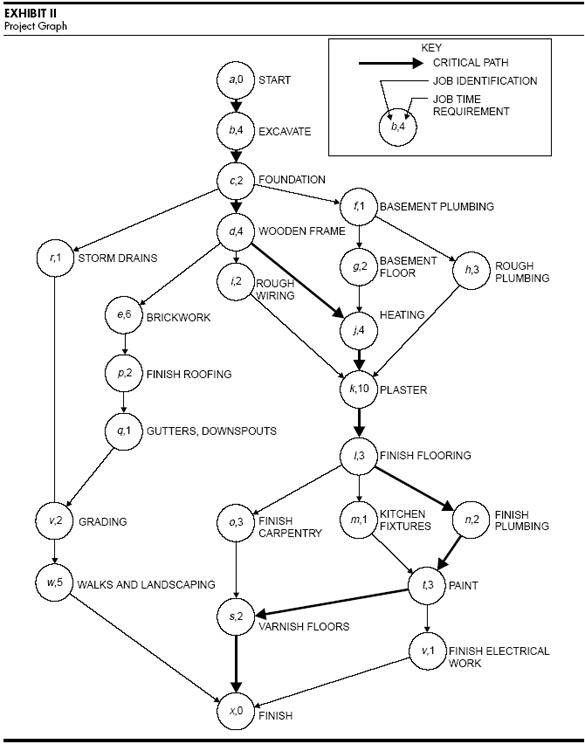
Here is another example of a crucial path from the Harvard Business Review, this time for the building of a house. Each circle in the CPM diagram represents a project activity and its duration, and the arrows in bold connect the activities on the critical path. There will be more concurrent tasks, like in this example, as projects get more complicated.
How to Find Critical Path of a Project?
1.Consider all Project Tasks:
You might as well use Work Breakdown Structure
2.Determine Task Dependencies
Before starting any task, identify those that depend on others. Utilize your judgement and the suggestions of your team.
3. Make a Critical Path Diagram (CPD)
A network diagram or critical path demonstrates the order of the tasks and activities.
4. Projected Timeline
You must estimate how long each task will take before applying the critical path method. Utilize information from previous projects and other resources, such as subject matter experts.
5. Use the Critical Path Algorithm (CPM)
There are two passes in the critical path algorithm: a forward pass and a backward pass.
Forward Pass
The earliest start (ES) and earliest end (EF) of each activity are determined using the network diagram and the predicted time of each activity (EF). An activity’s ES is equal to its predecessor’s EF, and its EF is calculated using the formula EF = ES + t. (t is the activity duration). The estimated time needed to finish the full project is specified in the EF of the final activity.
Backward Pass
starts by designating the latest finish of the previous activity as its earliest finish. You can calculate the LS is using the formula LS = LF – t. (t is the activity duration). The LF for the subsequent activity is the earliest of the start times for the preceding activities.
6. Determine whether each activity has a float or slack.
To calculate the float or slack of each task, use this formula. LS – ES = Float
Figure out the Critical Path.
With the exception of the first task in your CPM plan, each of these critical path activities is dependent on the others. Parallel tasks to the critical path activities are all project tasks that have positive slack.
You might also like: WHAT IS EARNED VALUE IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT
